Asset allocation represents a pivotal strategy in personal and institutional investment planning as it refers to how an investor chooses to apportion his or her portfolio amongst the several asset classes comprising stocks, bonds, real estate, and cash. This approach not only influences the risk factor of investment returns but is fundamentally very basic in managing such risk.
Definition and Concept of Asset Allocation
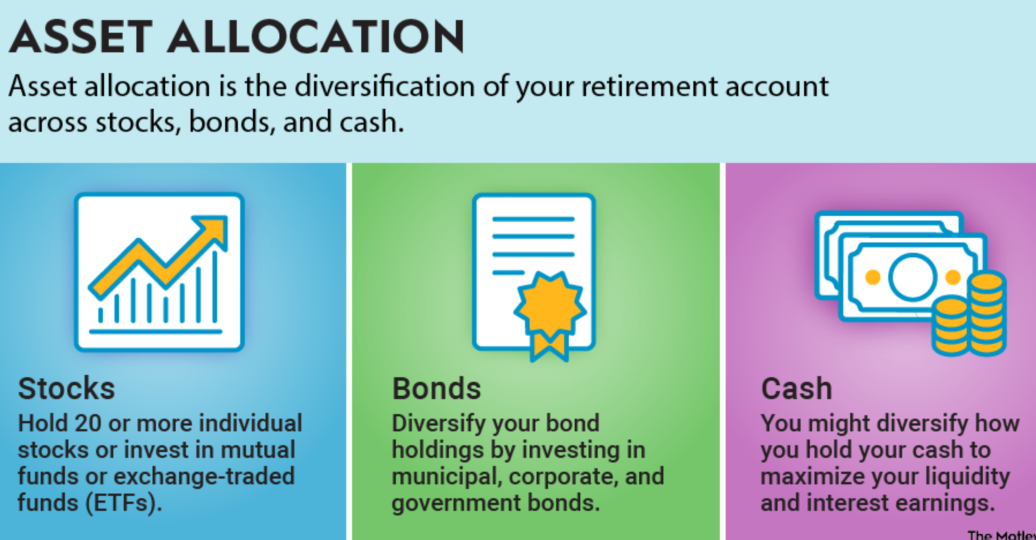
Finding the ideal balance between risk and return by distributing assets across several asset classes is known as asset allocation. It basically entails determining the proportion of any portfolio that should go to each asset class in light of the investor's risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial objectives.
Young investors with a very long time horizon might favor equities as the optimal asset class to generate higher growths; retirees, on the other hand, would prefer bonds and cash as more stable sources of income.
Benefits of Asset Allocation
Diversification Decreases Risk
Asset allocation allows the distribution of investments across various asset classes, thereby minimizing losses due to any loss in a specific asset class. The positive returns of another asset class might off-set any loss that may be incurred due to underperformance by one class, thus smoothing the portfolio ride of the entire investment.
A good asset allocation strategy searches for the highest possible return for a targeted level of risk. One can, for example, mix high-risk assets, like equities, with low-risk ones, bonds, and achieve a balanced approach responsive to whatever change may occur in the market. .
Market Conditions
Economic and market trends can also have an impact on asset allocation. For instance, when interest rates become low, investors cut down their bond allocations and prefer more toward equities or direct real estate for better returns.
Type of Asset Classes in Allocation
Equities
Equities have a natural probability of growth but have generally higher volatility. It is helpful for long-term situations, such as retirement planning.
Fixed-Income Investments
Bonds and other similar types of investments can provide a stable flow of income, making them ideal for risk-adverse investors or approaching retirement.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
They allow liquidity and safety regarding the returns, though tend to be lower. They really find a place in emergency funds or short-term objectives.
Alternative Investments
Some level of diversification can add to the portfolio from real estate or commodities or private equity investments. Their risk is, however, on the higher side, and liquidity is very limited in most instances.
Periodic Rebalancing: Keeping Asset Allocation Effective
Market fluctuations can move asset classes in a portfolio in different directions from the desired target. Routine rebalancing-buying and selling investments to restore the portfolio to its intended asset allocation-maintains the portfolio consistent with the investor's objectives and risk capacity. Conclusion
Asset allocation is the backbone of any thriving investment strategy. It ensures that the risk versus return balance is maintained, diversification occurs across asset classes, and goals are in line with financial planning. Asset allocation hence helps investors come out "float" during untold market uncertainty, paving the way to long-term success for novices and experienced investors alike.

